We can solve the given equation for x in terms of y as follows x y xy = 1 (Given) Add "‒y" to both sides x y xy (‒y) = 1 (‒y) Using the Commutative Property of Addition on the left side, we have x xy y (‒y) = 1 (‒y)So from the graph we can see that the slope is (which tells us that in order to go from point to point we have to start at one point and go up 1 units and to the right 1 units to get to the next point) the yintercept is (0,)and the xintercept is (,0) We could graph this equation another waySimple and best practice solution for xyxy=1 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,

Multiplicative Inverse Wikipedia
Y x 10
Y x 10-F 1 (f (x)) = log b (b x) = x Natural logarithm (ln) Natural logarithm is a logarithm to the base e ln(x) = log e (x) When e constant is the number or See Natural logarithm Inverse logarithm calculation The inverse logarithm (or anti logarithm) is calculated by raising the base b to the logarithm y x = log1 (y) = b y LogarithmicCheck out The LambertW function with Fematika, https//youtube/LkJAZXMAKz0 Also try Pythagorean's Triples https//youtube/n6vL2KiWrD4 , Making exponent an


Linear Inequalities How To Graph The Equation Of A Linear Inequality
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge andGraph y=x^21 Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Rewrite the equation in vertex form Tap for more steps Complete the square for Tap for more steps Use the form , to find the values of , , and Consider the vertex form of a parabolaSolution Steps y = x1 y = x − 1 Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side x1=y x − 1 = y Add 1 to both sides Add 1 to both sides
Weekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelledSimple and best practice solution for xyxy1=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,(1) a 11 x 1 a 12 x 2 = b 1 a 12 x 1 a 22 x 2 = b 2 where a 11, a 12, a 21, a 22, b 1, and b 2 are given numbers The solution of system (1) can be obtained by using determinants Here it is assumed that the determinant in the denominator differs from zero
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyGraphing the line y = x 3 on a Cartesian Graphgraph the function y=x3May 22, 16 · x = y/(1y), which is a function Isolate x as follows y = x/(x1) = ((x1)1)/(x1) = 11/(x1) So, adding (1/(x1) y) to both ends we find 1/(x1) = 1y Taking reciprocals of both sides we get x1 = 1/(1y) Subtracting 1 from both sides we get x = 1/(1y)1 = (1(1y))/(1y) = y/(1y) This uniquely determines x for any chosen value of y (except y=1 where it's not defined at all),
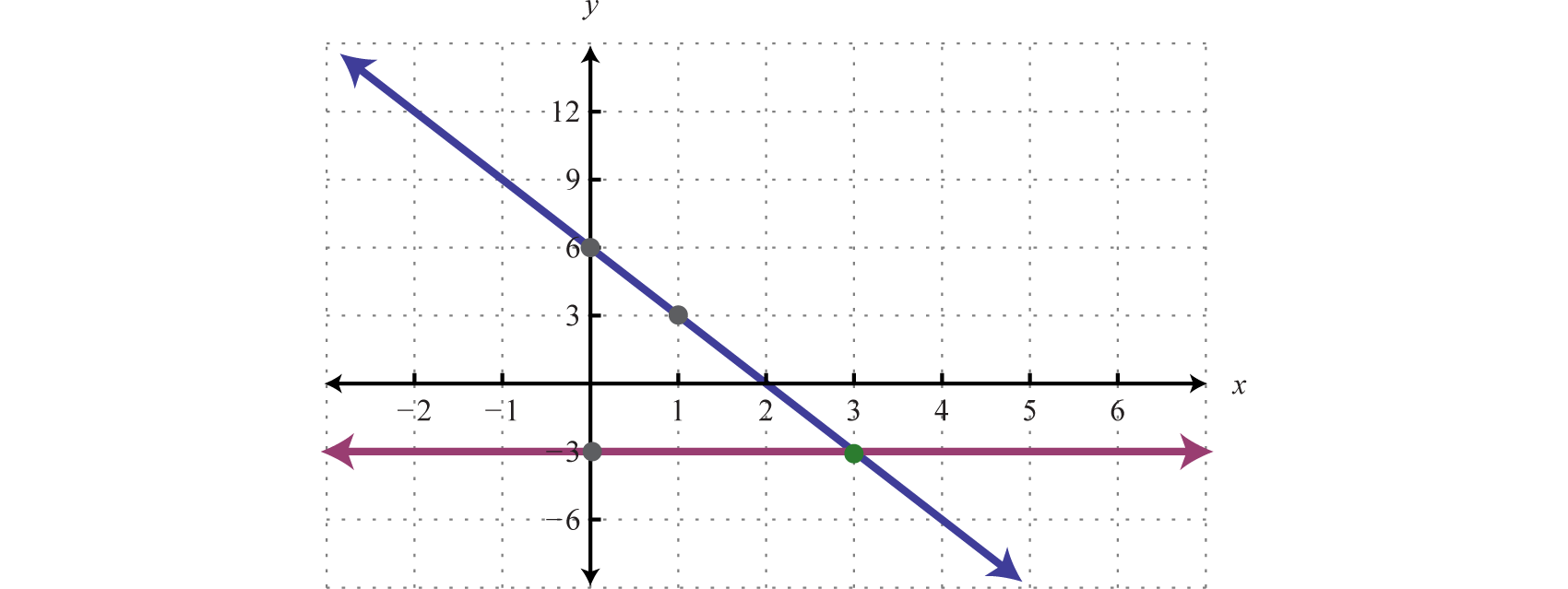


Linear Systems With Two Variables And Their Solutions


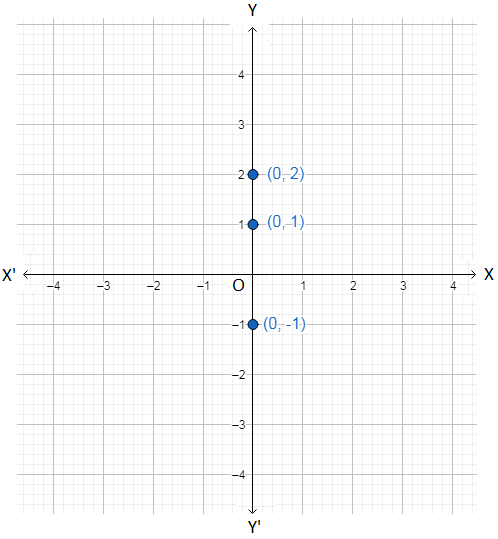
Write The Equation For A Linear Function From The Graph Of A Line College Algebra
It means a function x of x1x*(x1) is rightUse the ^ (caret) for exponentiation x^2 means x squared x/2y means Resources Simplifier Portal, help with entering simplifier formulas (a must read)Y=x en Related Symbolab blog posts Middle School Math Solutions – Equation Calculator Weekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelled User Data Missing Please contact supportLearn how to use the Algebra Calculator to check your answers to algebra problems Example Problem Solve 2x3=15 Check Answer x=6 How to Check Your Answer with Algebra Calculator First go to the Algebra Calculator main page Type the following



If X 1 Y Y 1 X 0 Then Prove That 1 X 2 Dydx 1 0



Solved Solve Dy Dx 1 X Y Solve Dy Dx Y X 1 Y Solve The In Chegg Com
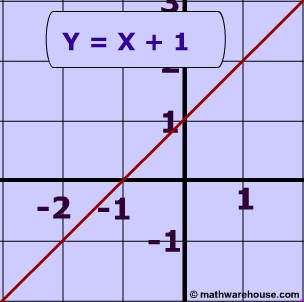
To write 1 y 1 y as a fraction with a common denominator, multiply by x x x x 1 x ⋅ y y 1 y ⋅ x x 1 x ⋅ y y 1 y ⋅ x x Write each expression with a common denominator of xy x y, by multiplying each by an appropriate factor of 1 1 Tap for more steps Multiply 1 x 1Simple and best practice solution for Y=x1 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,For example, when x is 1 y = 2×1 1 = 3 Check for yourself that x=1 and y=3 is actually on the line Or we could choose another value for x, such as 7 y = 2×7 1



Systems Of Equations With Graphing Article Khan Academy


Graph Of Standard Linear Relations Between X Y Graph Of Y X
How do you graph y=x1graphing y=x1 video instructionWeekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelled User Data Missing Please contact support We want your feedback (optional) (optional) Please add a message Message received Thanks for the feedbackCombine all terms containing y \left (1x\right)y=x ( 1 − x) y = − x Divide both sides by 1x Divide both sides by 1 − x \frac {\left (1x\right)y} {1x}=\frac {x} {1x} 1 − x ( 1 − x) y = − 1 − x x Dividing by 1x undoes the multiplication by 1x Dividing by 1 − x undoes the multiplication by 1 − x



Algebra Calculator Tutorial Mathpapa
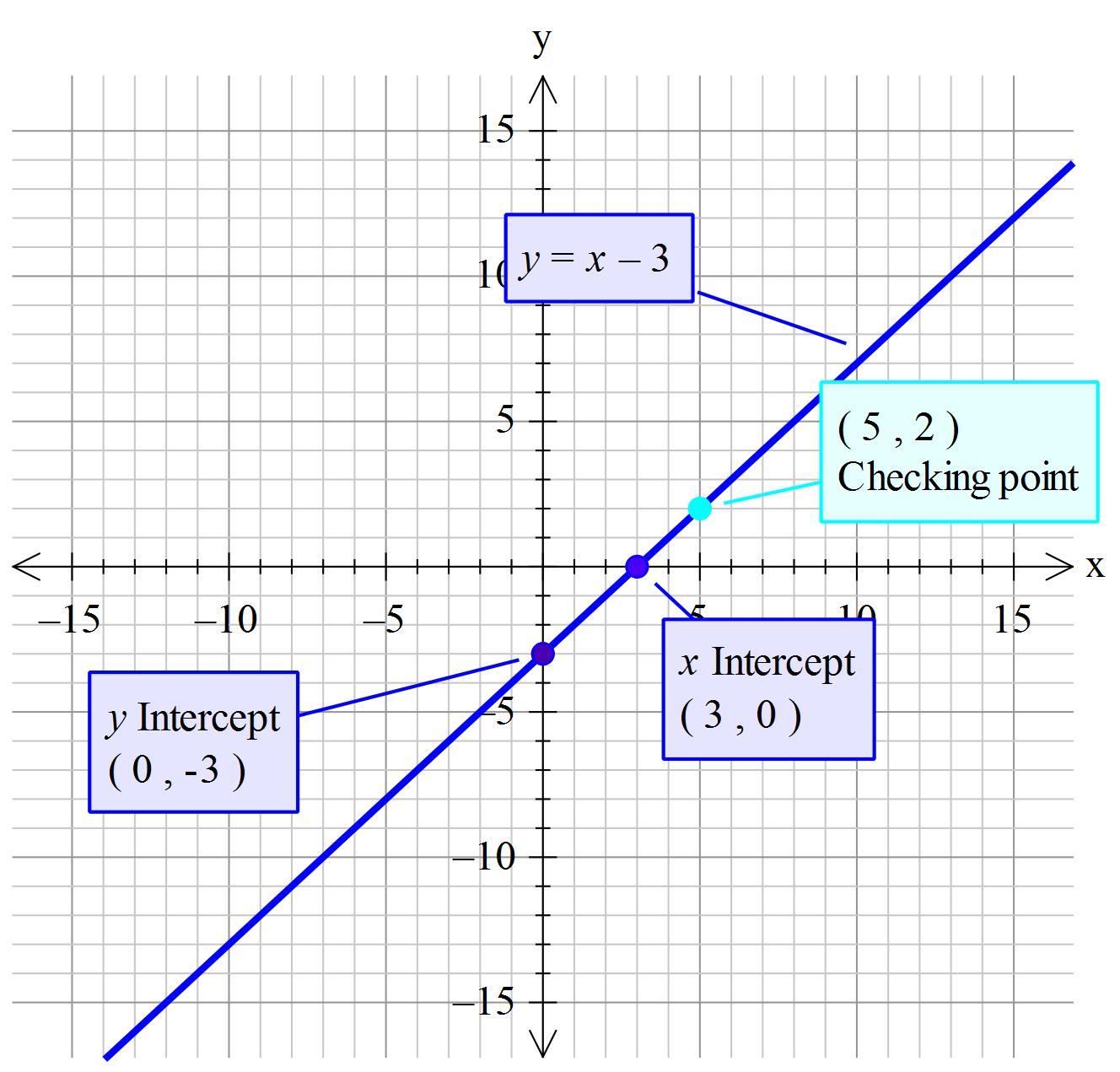


How Do You Graph Y X 3 Example
You must use the "*" (star) symbol for all multiplications!x(x1) is WRONG!In this free online math video lesson on Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution we solve each system by substitution We solve 2x3y=1 and y=x1 by suMay 02, 17 · Find an answer to your question if x/y y/x = 1 then find x^3 y ^3 lalalalaaaaaa how are you guys good bye forever miss you all stay home , stay safe ,happy
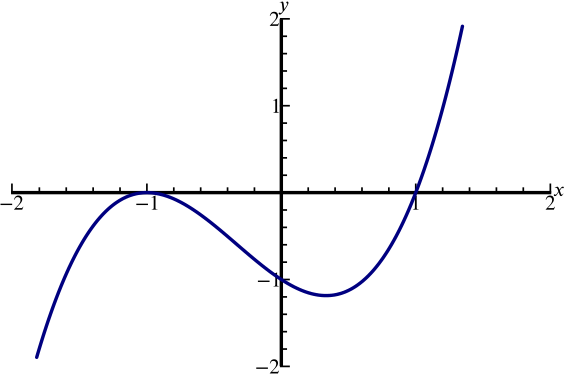


Solution Can We Sketch The Graph Y X 3 X 2 X 1 Polynomials Rational Functions Underground Mathematics



D1 Y 2x 3 D2 Y X 2 D3 Y X 1 D4 Y 3 4 X Ppt Telecharger
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyGraph y=x1 Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for is Tap for more steps To find the coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value equal to In this case, Add to both sides of the equation Replace the variable with in the expressionCalculus Applications of Definite Integrals Determining the Volume of a Solid of Revolution 1 Answer Frederico Guizini S Apr 2, 17 See the
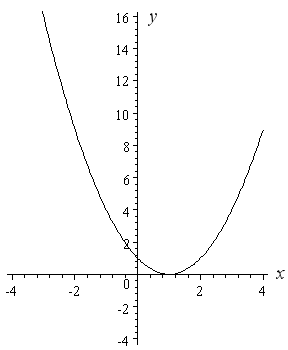


How To Draw Y 2 X 2
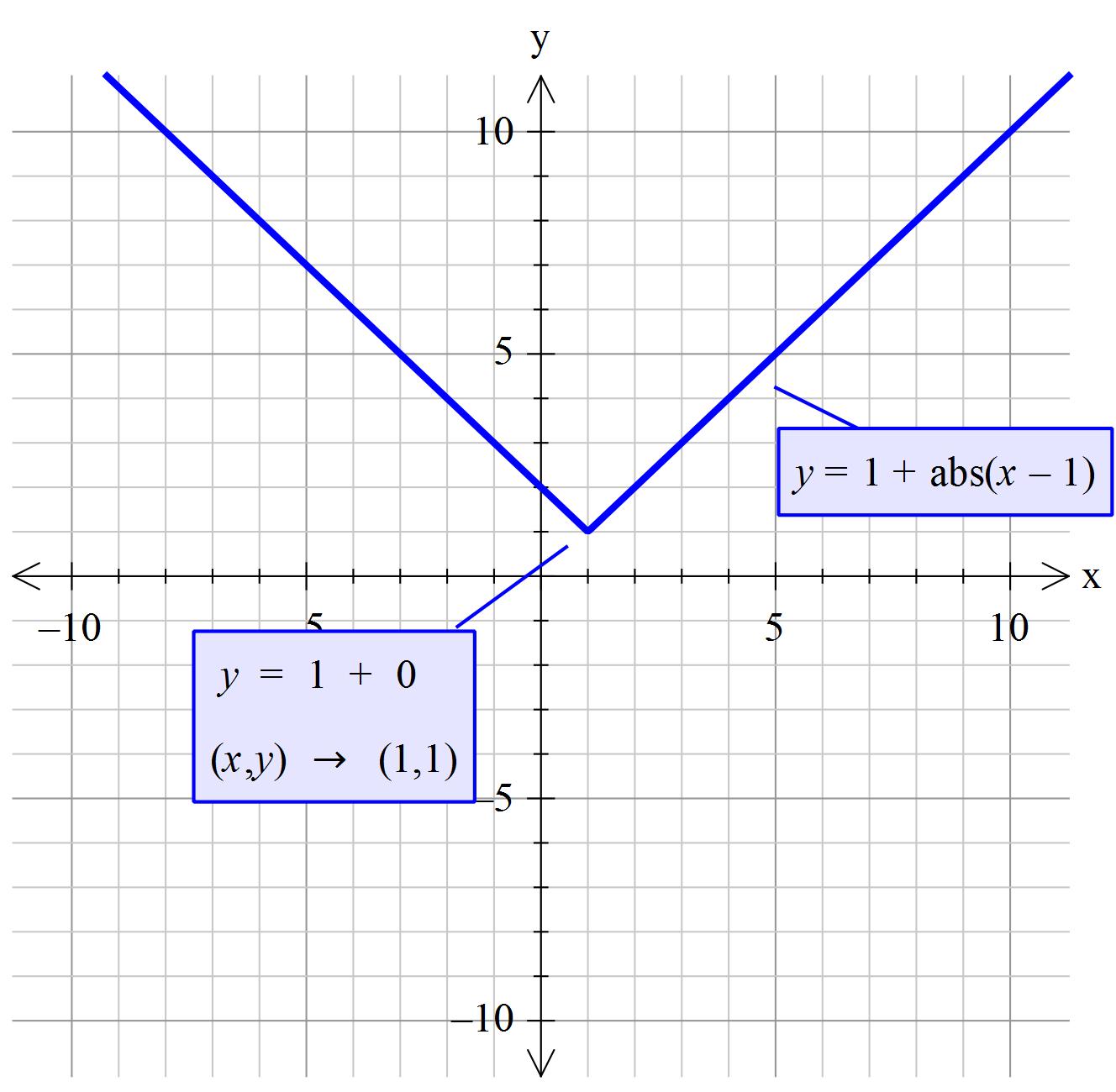


How Do You Graph Y 1 X 1 Socratic
X•(y1)•(y1) —————————————— • xy = 0 • xy xy Now, on the left hand side, the xy cancels out the denominator, while, on the right hand side, zero times anything is still zero The equation now takes the shape x • (y1) • (y1) = 0 Theory Roots of a productGraph y=x1 Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is , where is the slope and is the yintercept Find the values of and using the form The slope of the line is the value of , and the yintercept is the value of SlopeCheck x 2 is the square of x 1 Factorization is (y x) • (y x) 73 Rewrite (xy) as (1) • (yx) Canceling Out 74 Cancel out (yx) which now appears on both sides of the fraction line Step 8 Pulling out like terms 81 Pull out like factors y x = 1 • (y x) Final result y x



Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver


Solution Solve By Graphing X Y 1 X Y 1
Solution for xy=1 equation Simplifying x 1y = 1 Solving x 1y = 1 Solving for variable 'x' Move all terms containing x to the left, all other terms to the right Add 'y' to each side of the equation x 1y y = 1 y Combine like terms 1y y = 0 x 0 = 1 y x = 1 y Simplifying x = 1 yDec 04, 17 · Hence, in our problem, xintercept #= 1# Hence our line will pass through two points #(1,0) and (0,1)# You may want to investigate the graph for a better understandingStep 1 1 Simplify — x Equation at the end of step 1 1 — ÷ 1 ÷ y x Step 2 1 Divide — by 1 x Equation at the end of step 2 1 — ÷ y x Step 3 1 Divide — by y x Final result 1 —— xy
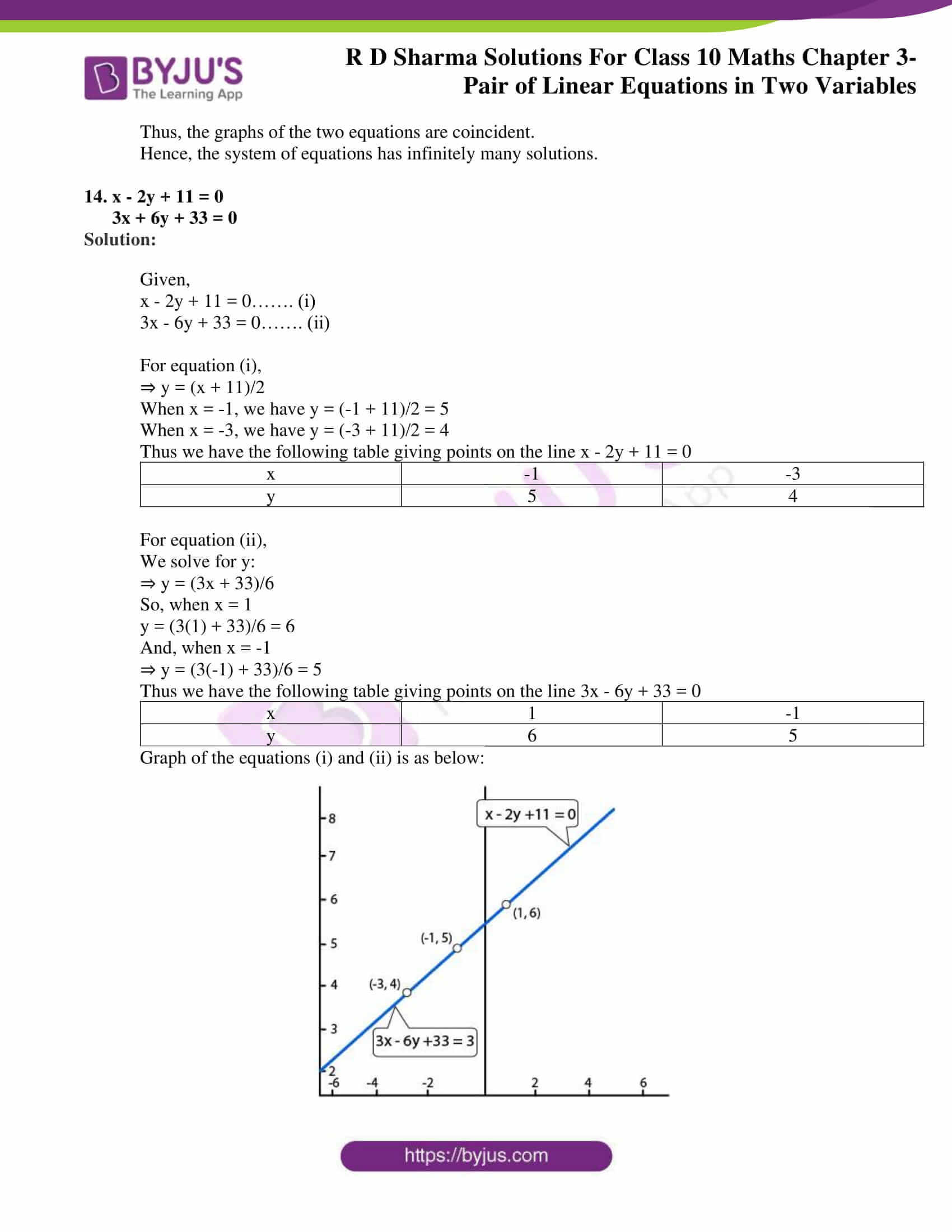


Rd Sharma Class 10 Solutions Maths Chapter 3 Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Exercise 3 2



Example 1 If X 1 Y 2 3 1 Find X And Y Class 11
Apr 02, 17 · How do you find volume by rotating area enclosed by #y=x^3# and #y=sqrt(x)# about x=1?Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge andWeekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelled User Data Missing Please contact support We want your feedback (optional) (optional) Please add a message Message received Thanks for the feedback


Champ De Vecteurs Html


Multiplicative Inverse Wikipedia
Add 1 to both sides Add 1 to both sides 2x=y1 2 x = y 1 Divide both sides by 2 Divide both sides by 2 \frac {2x} {2}=\frac {y1} {2} 2 2 x = 2 y 1 Dividing by 2 undoes the multiplication by 2Y ~ x y ~ 1 x Here are ways to give a linear regression of y on x through the origin (that is, without an intercept term) y ~ 0 x y ~ 1 x y ~ x 1 In the specific case you mention ( y ~ 1 ), y is being predicted by no other variable so the natural prediction is the mean of y, as Paul Hiemstra statedFind the X and Y Intercepts y=x1 y = −x − 1 y = x 1 Find the xintercepts Tap for more steps To find the xintercept (s), substitute in 0 0 for y y and solve for x x 0 = − x − 1 0 = x



Multiplicative Inverse Wikipedia


Reflection In The Line Y X Geogebra
Variable x cannot be equal to − 1 since division by zero is not defined Multiply both sides of the equation by x 1 y\left (x1\right)=xy\left (x1\right)y y ( x 1) = x y ( x 1) y Use the distributive property to multiply y by x1 Use the distributive property to multiply y by x 1Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historySimple and best practice solution for 1/x1/y equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,
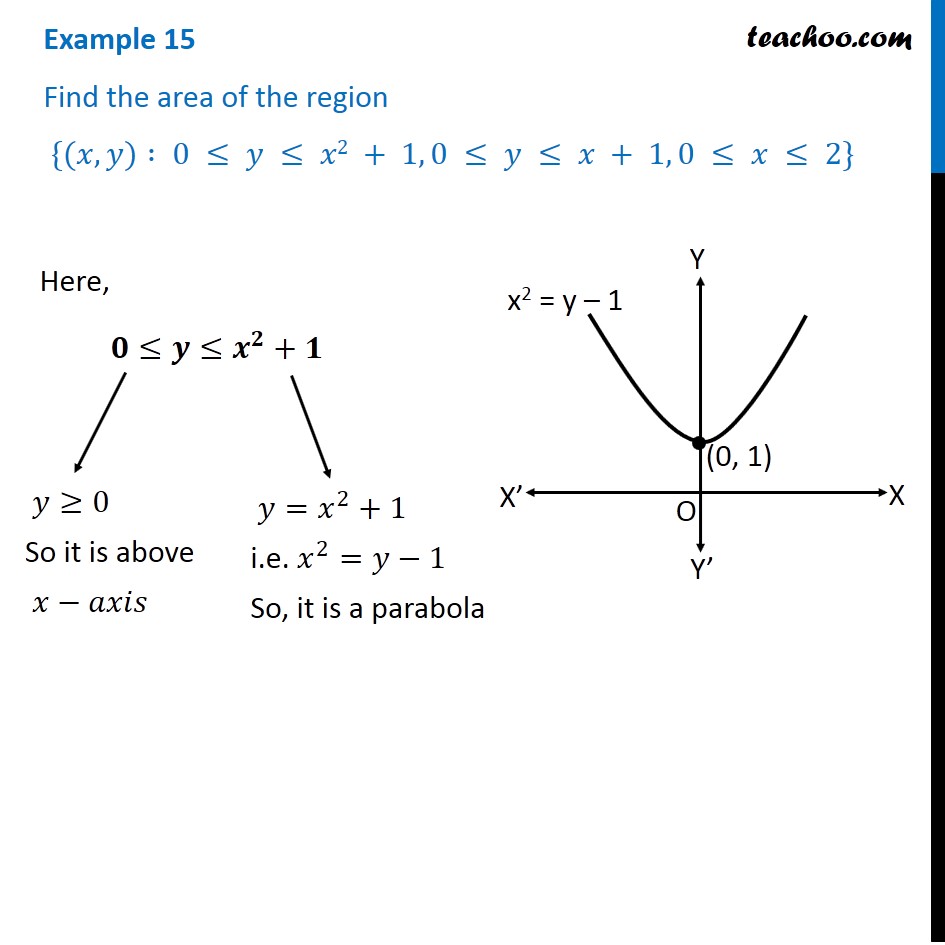


Example 15 Find Area X Y 0 Y X2 1 0 Y X



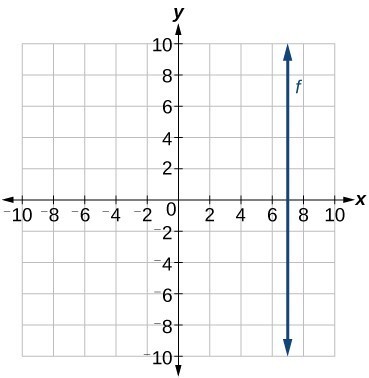
Y X 1 E Y X 1
2xy=1 Geometric figure Straight Line Slope = 2 xintercept = 1/2 = yintercept = 1/1 = Rearrange Rearrange the equation by subtracting what is to the right of the Given that 1 = 27 \times 11 74 \times 4, solve the following equations in modulo 74 3x y = 1Plot of the six trigonometric functions, the unit circle, and a line for the angle θ = 07 radians The points labelled 1, Sec(θ), Csc(θ) represent the length of the line segment from the origin to that point Sin(θ), Tan(θ), and 1 are the heights to the line starting from the xaxis, while Cos(θ), 1, and Cot(θ) are lengths along the xaxis starting from the origin
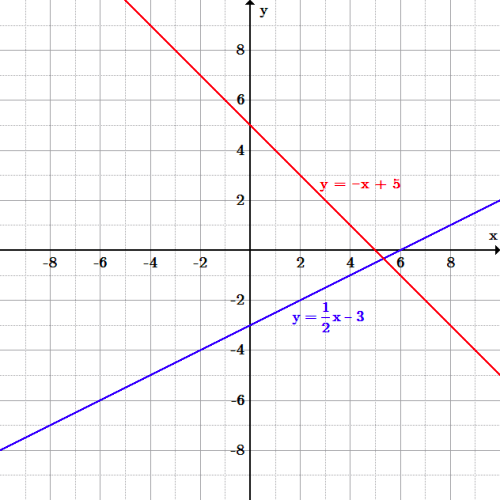


Introduction To Linear Functions Boundless Algebra



How To Plot 3d Graph For X 2 Y 2 1 Mathematica Stack Exchange



Basics Of Solving Equations In Sympy By Joshua Siktar The Startup Medium


Graph Y X 2 Youtube
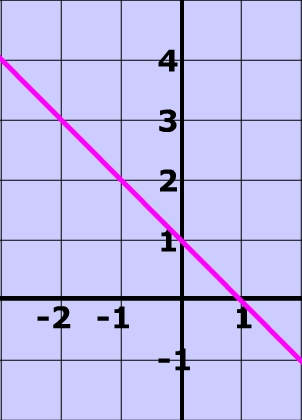


Linear Inequalities How To Graph The Equation Of A Linear Inequality


Solve For X And Y X 1 2 Y 1 3 9 X 1 3 Y 1 2 8 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Finding Linear Equations



Graphing Linear Inequalities



Math Spe Exercices Sur Les Equations Differentielles
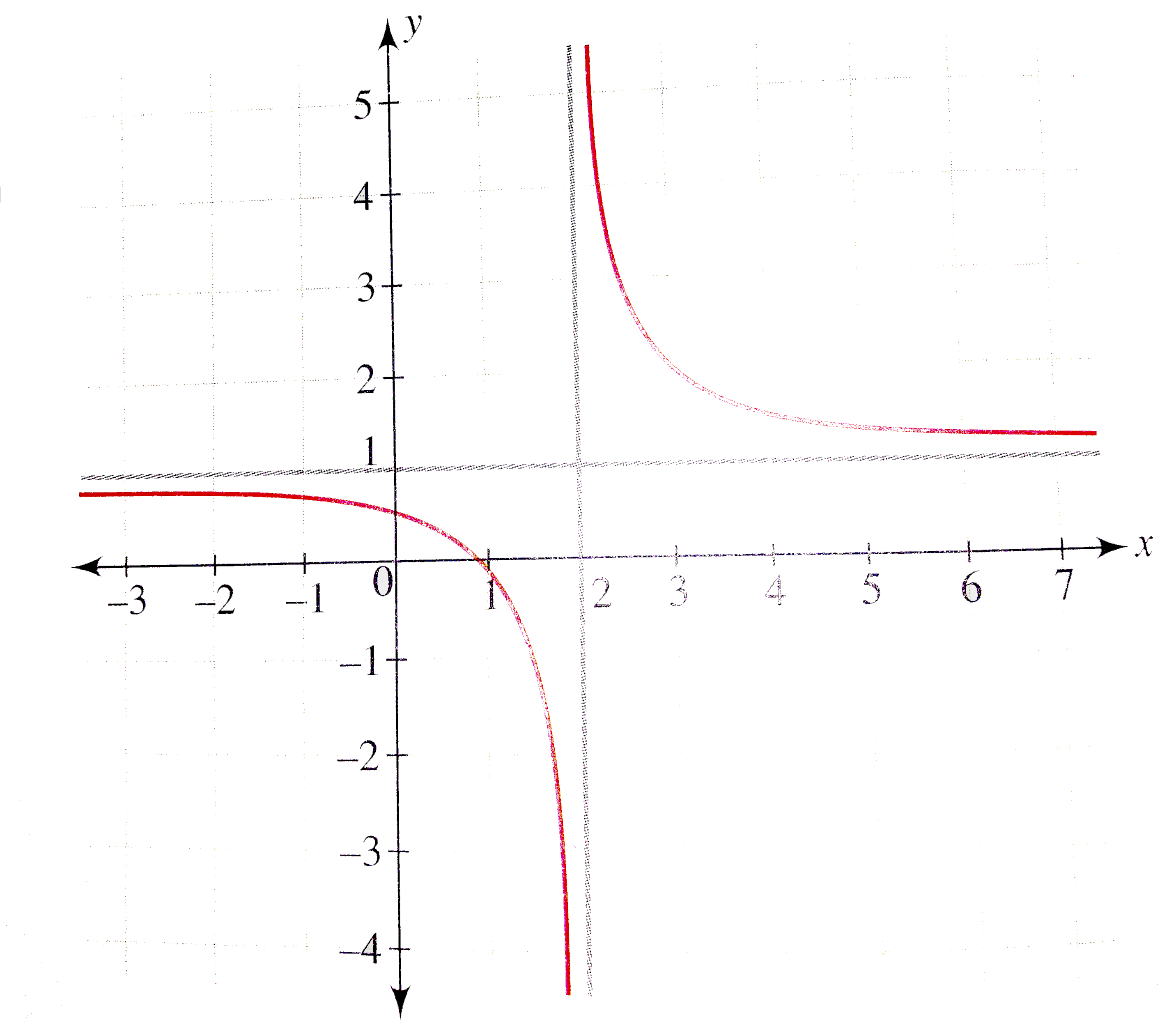


Draw The Graph Of Y X 1 X 2



Draw The Graph Of Linear Equations Y X And Y X On The Same Certesian Plane What Do You Observed Brainly In



What Will The Graph Of Y 1 X Be Quora



D1 Y 2x 3 D2 Y X 2 D3 Y X 1 D4 Y 3 4 X Ppt Telecharger
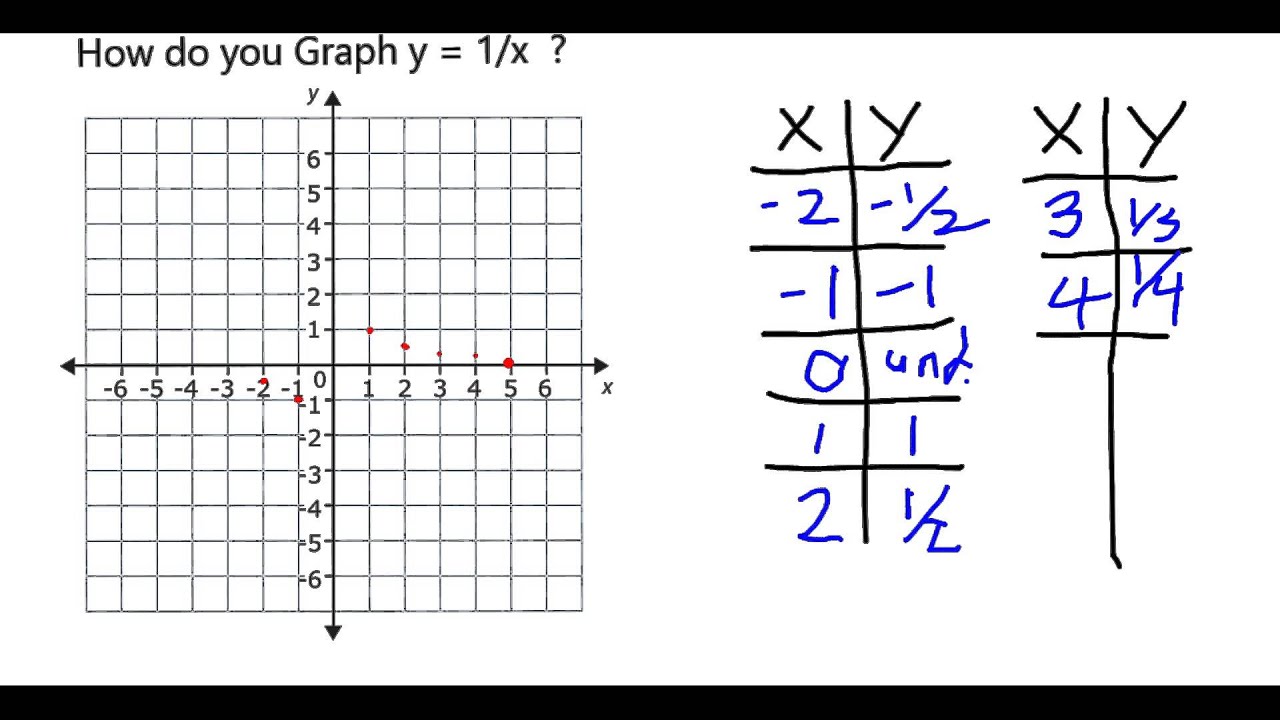


How Do You Graph Y 1 X Youtube


Mathematics Ske Text Unit G4 Section 4 Transformations Of Graphs Of Functions



Equations De Droites Maxicours



Linear Inequalities How To Graph The Equation Of A Linear Inequality


Graphing Equations Problems 2 Sparknotes


Function And Relation Library



X 1 2 Y 1 3 8 X 1 3 Y 1 2 9 Simultaneous Linear Equation Brainly In
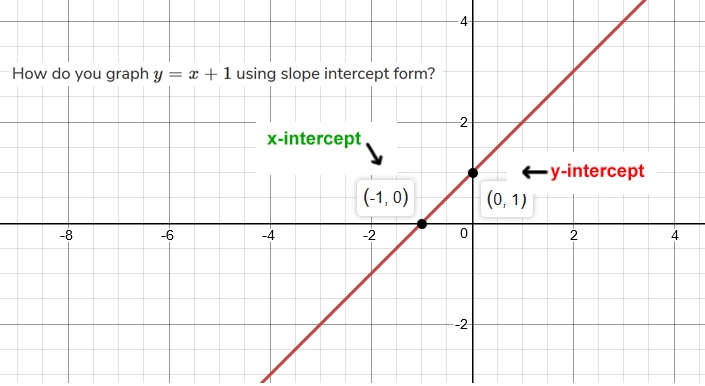


How Do You Graph Y X 1 Using Slope Intercept Form Socratic



The Area Bounded By The Curves Y X 1 2 Y X 1 2 And Y
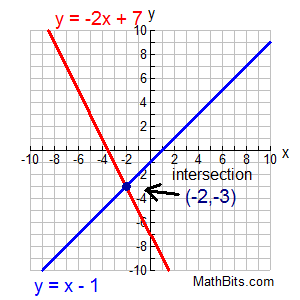


Systems Of Linear Equations Graphical Solution Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
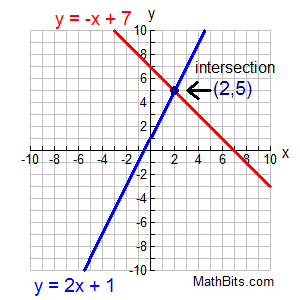


Systems Of Linear Equations Graphical Solution Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
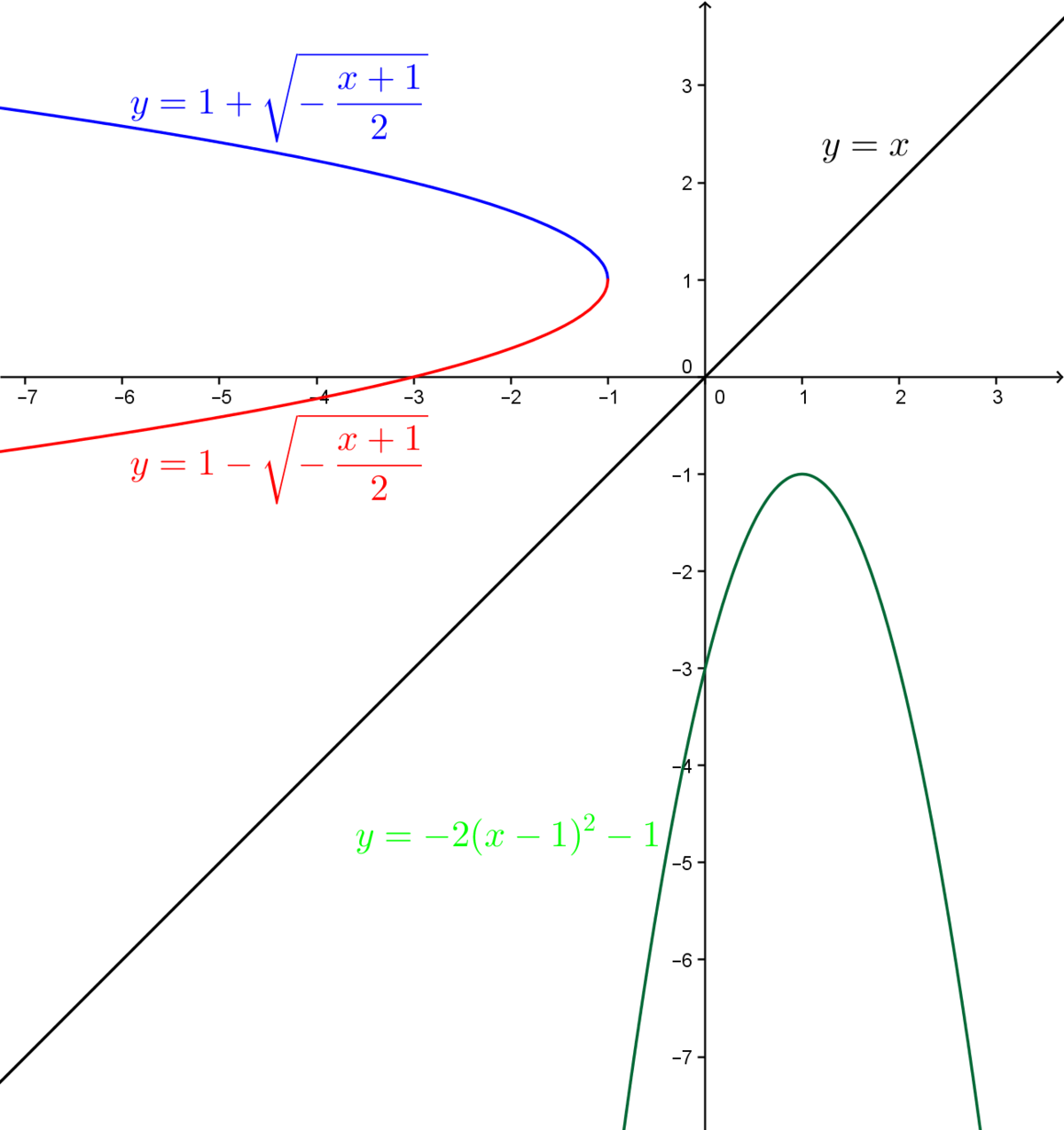


La Reciproque De La Fonction Polynomiale De Degre 2 Alloprof



Solved Solve Y Y X 2 1 Xy 6 0 With Y 1 1 S Chegg Com
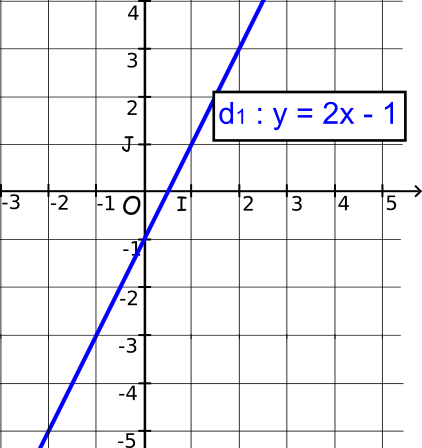


Cours Equations De Droites



Graphing Linear Functions Expii
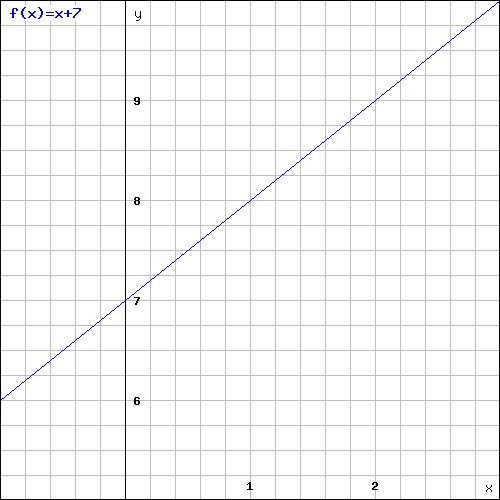


Functions And Linear Equations Algebra 2 How To Graph Functions And Linear Equations Mathplanet


Answer In Algebra For Patrick



Solve Y 1 Xy Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Slope Intercept Form Graphing Lines Free Math Help


Fonctions Reciproques
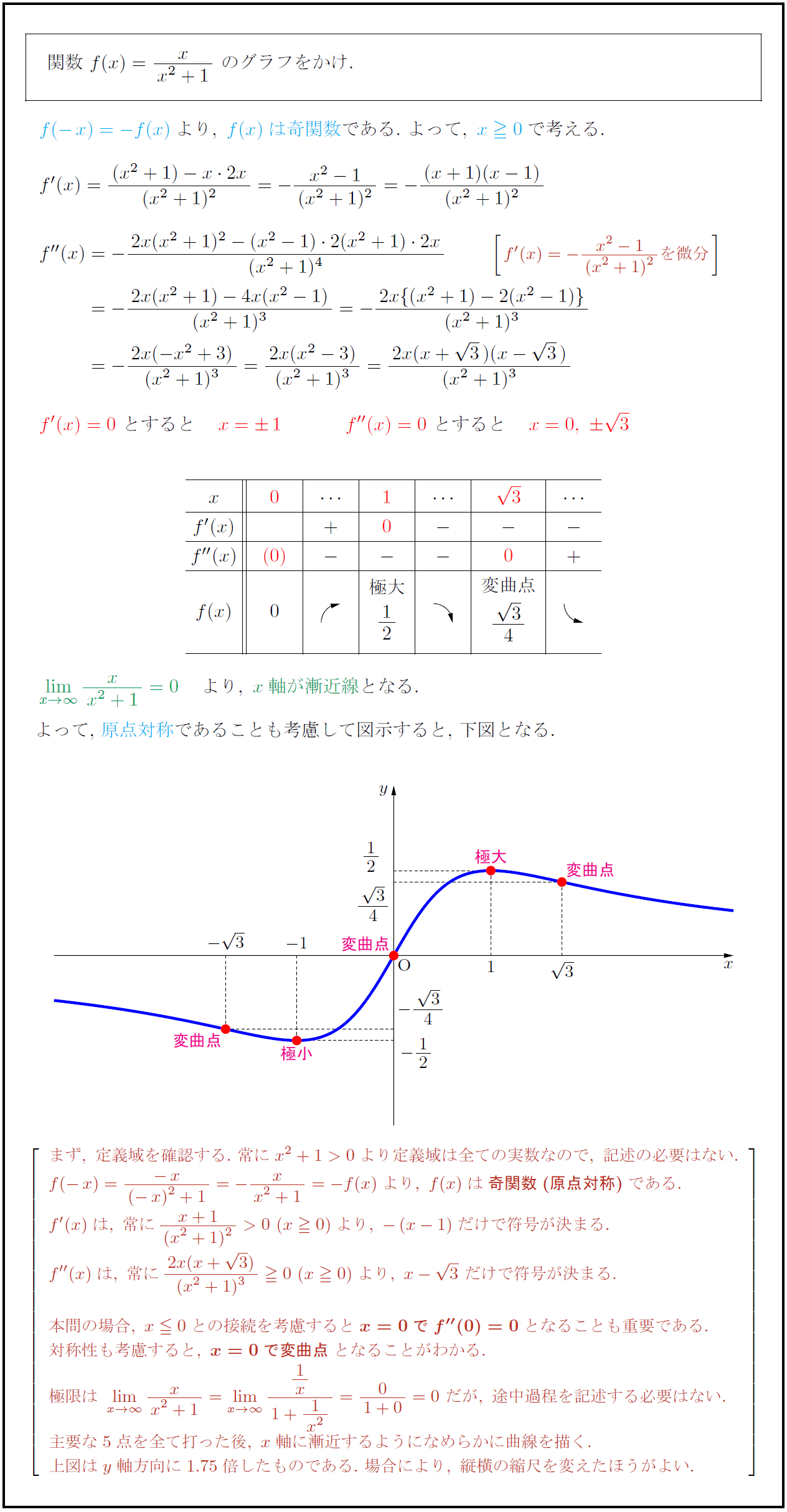


高校数学 分数関数 Y X X 1 のグラフ 受験の月


Solution How Do You Graph Y X 1



Explain How To Graph Y X 1 2 9 Using The Roots Y Intercept Symmetric Point And Vertex Study Com


Solution How Do You Graph The Function Y X 1
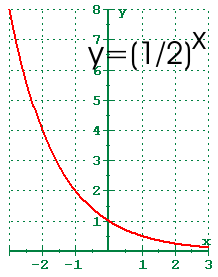


4 1 Exponential Functions And Their Graphs


Axe Centre De Symetrie
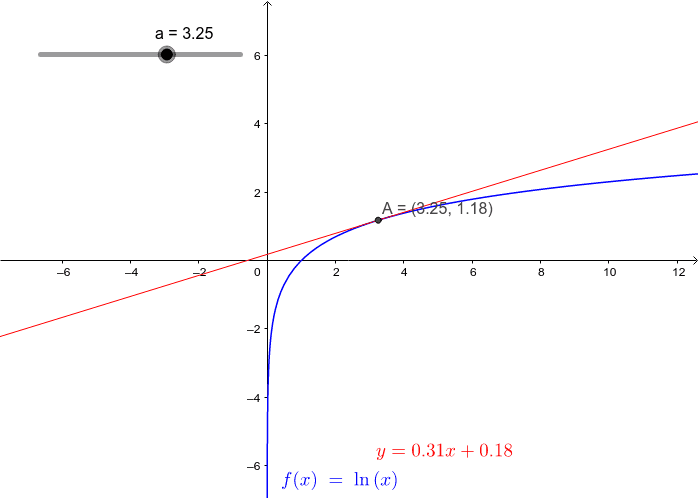


Derivative Of Y Ln X Geogebra



Content Finding Domains And Ranges
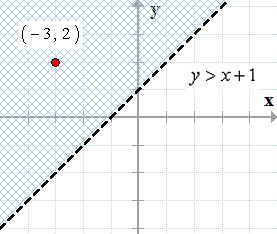


Graphing Linear Inequalities Chilimath



Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver



Ex 5 5 12 Find Dy Dx Xy Yx 1 Class 12 Cbse Ncert
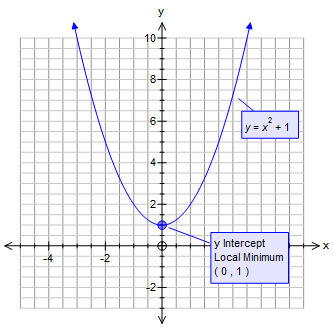


How Do You Graph Y X 2 1 Socratic


Graphing Linear Functions Expii


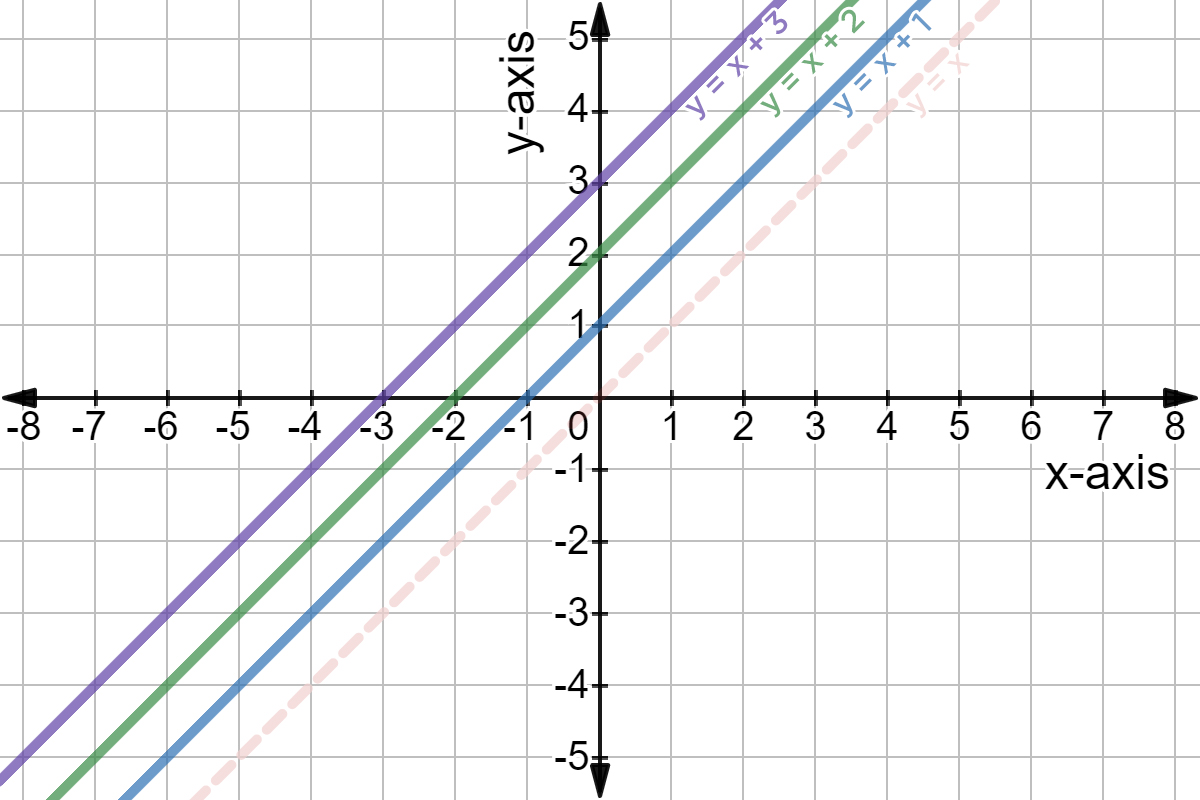
Rd Sharma Solutions Exercise 13 3 Chapter 13 Class 9 Linear Equations In Two Variables


Other Regressions
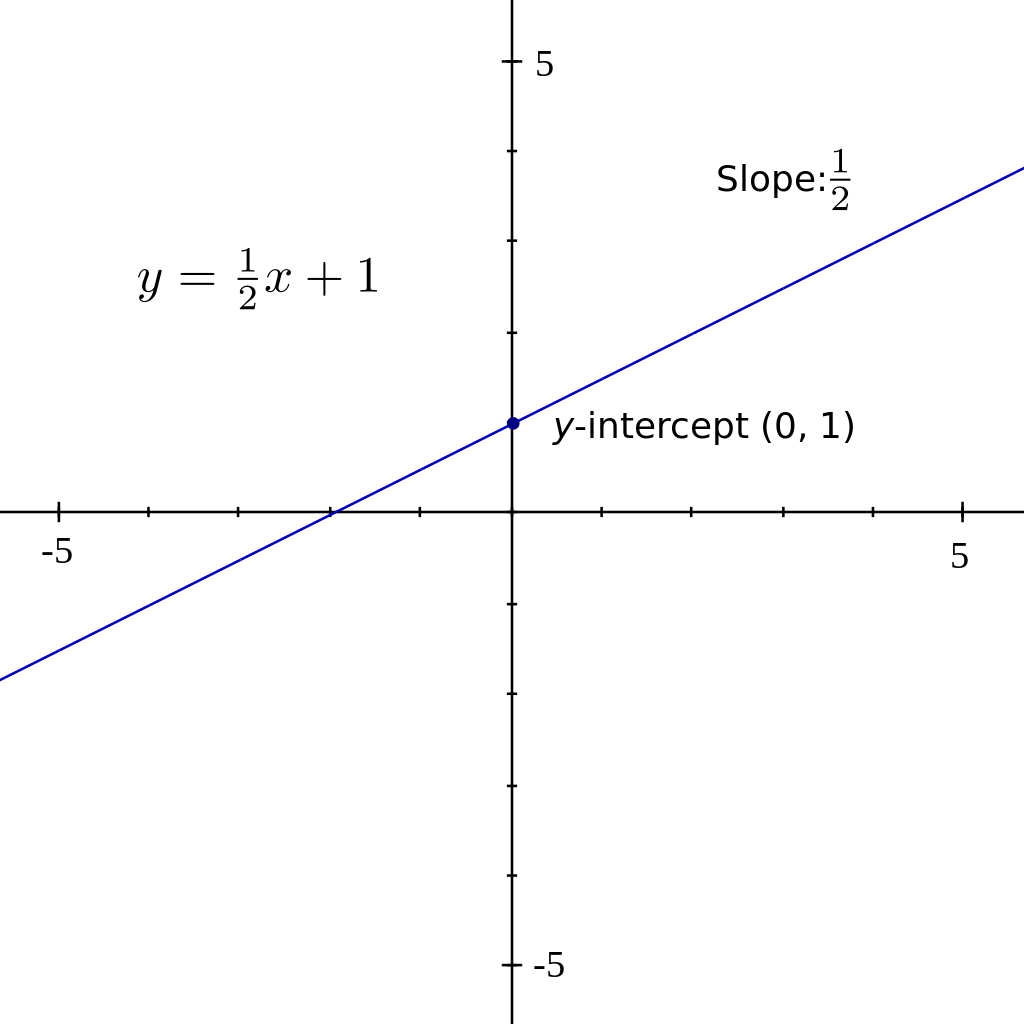


File Y 1 2 X 1 Svg Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
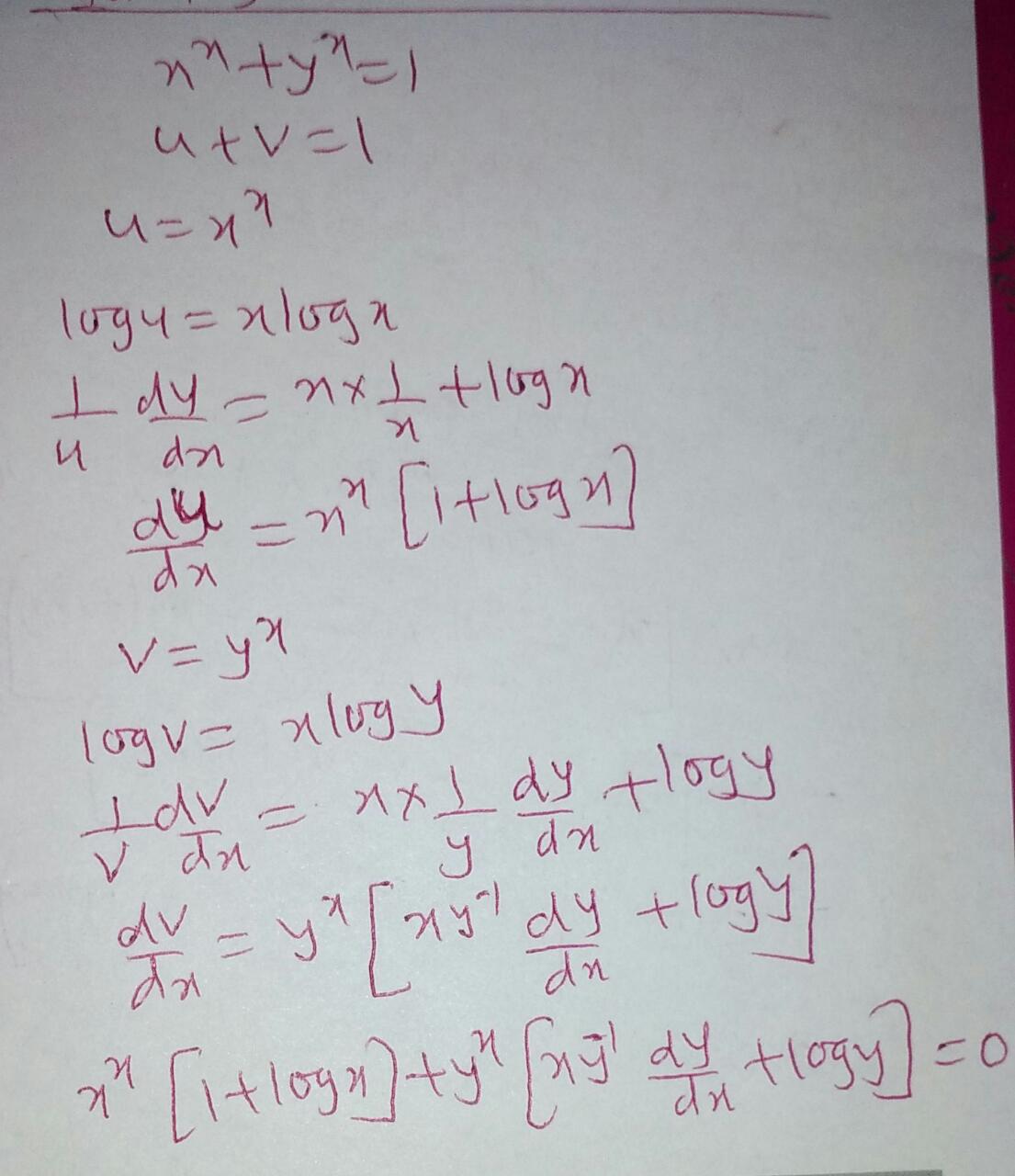


If Xx Yx 1 Show That Dy Dx Xx 1 Log X Yx Log Y Xyx 1 Mention Each And Every Formula And Minute Details Mathematics Topperlearning Com 78jts4
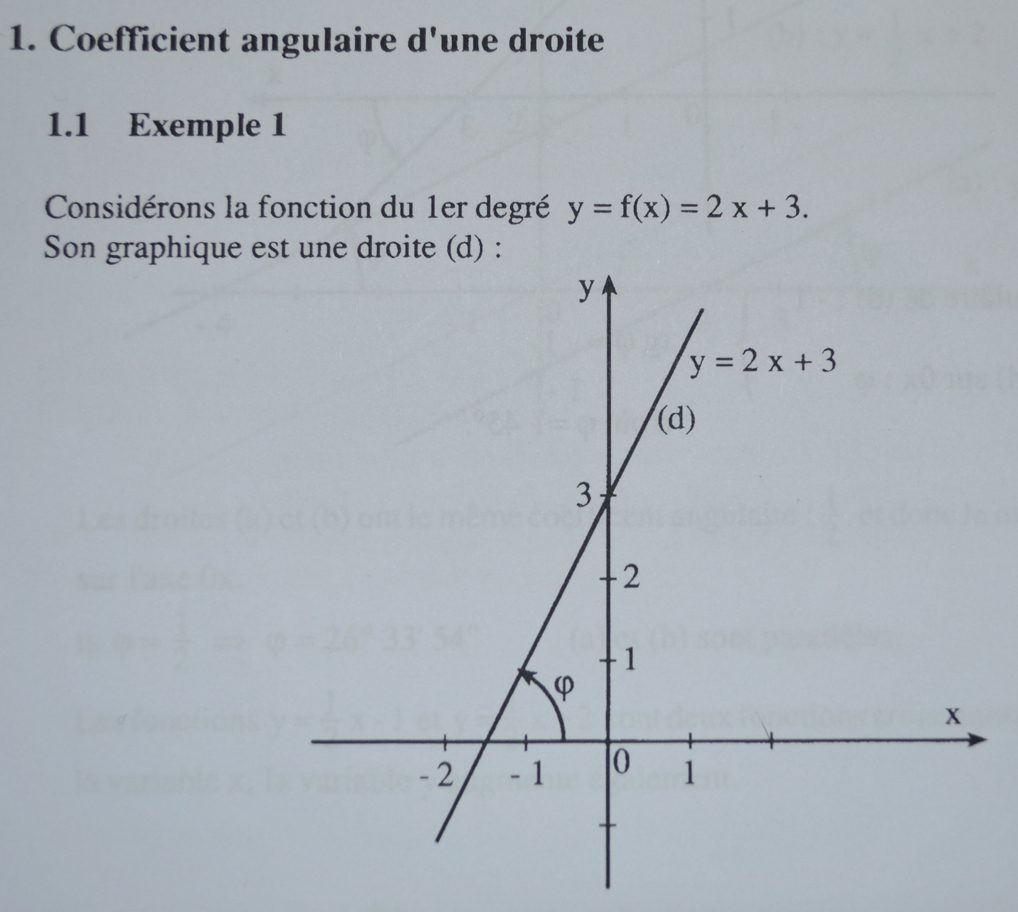


Representer Une Droite De Type Y X 1 Dans Repere Orthonorme



The Line Y X 1is A Tangent To The Curve Y 2 4xat The Point A
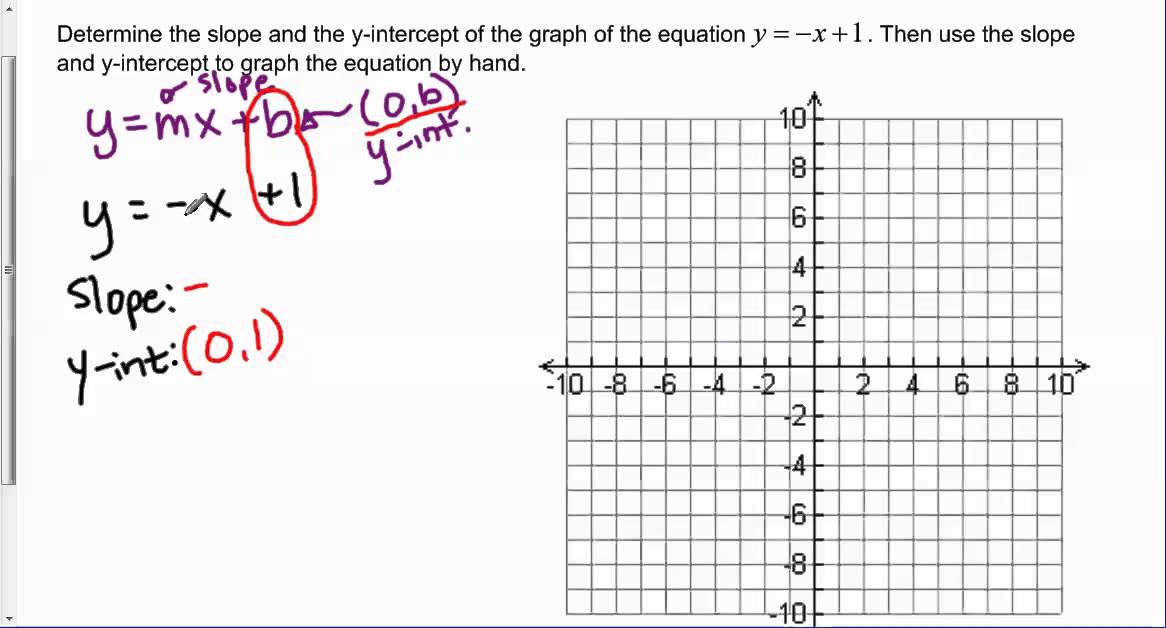


Determine The Slope And Y Intercept Of Y X 1 And Graph The Equation Youtube



If Y X X2 1 1 2 M Then Show That X2 1 D2y Dx2 X Dy Dx M2y 0 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 6jd9kell
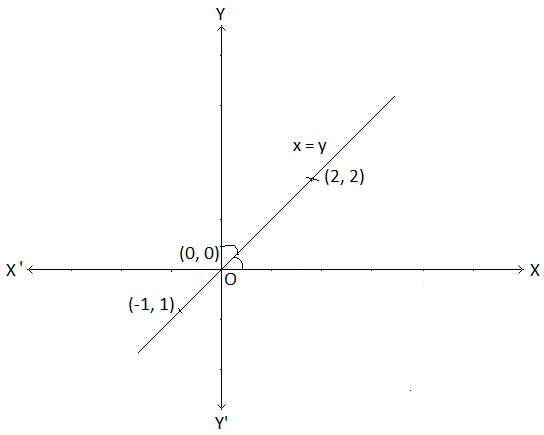


Graph Of Standard Linear Relations Between X Y Graph Of Y X


Quadratics Graphing Parabolas Sparknotes
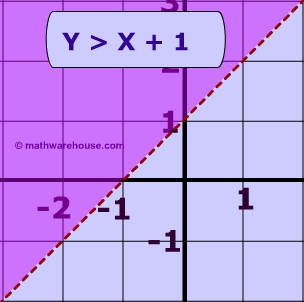


Linear Inequalities How To Graph The Equation Of A Linear Inequality



Solving Systems By Graphing And Substitution


Graphing Systems Of Inequalities


12 Courbes Usuelles


Linear Relationship Rules Passy S World Of Mathematics
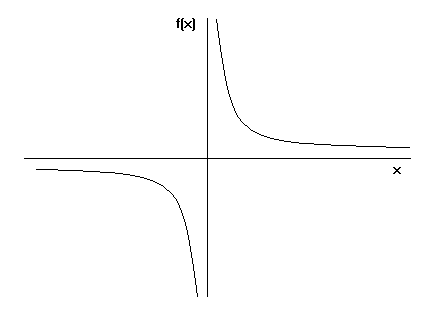


Functions Algebra Mathematics A Level Revision



Postroit Grafik Funkcii Y X 1 S Pomoshyu Grafika Najti A Znachenie X Esli Y 1 Shkolnye Znaniya Com
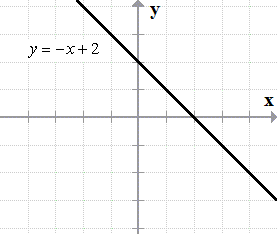


Graphing Linear Inequalities Examples Chilimath


How To Draw The Graph Of Y X And Y X In The Same Graph Quora
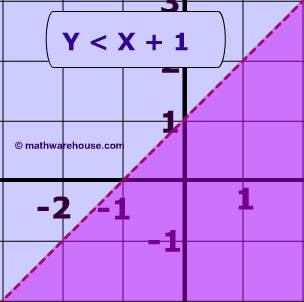


Linear Inequalities How To Graph The Equation Of A Linear Inequality
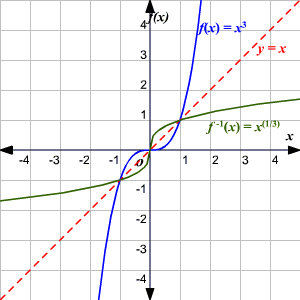


One To One Functions


Solution How Do You Graph Y X 1



Graphing Linear Inequalities
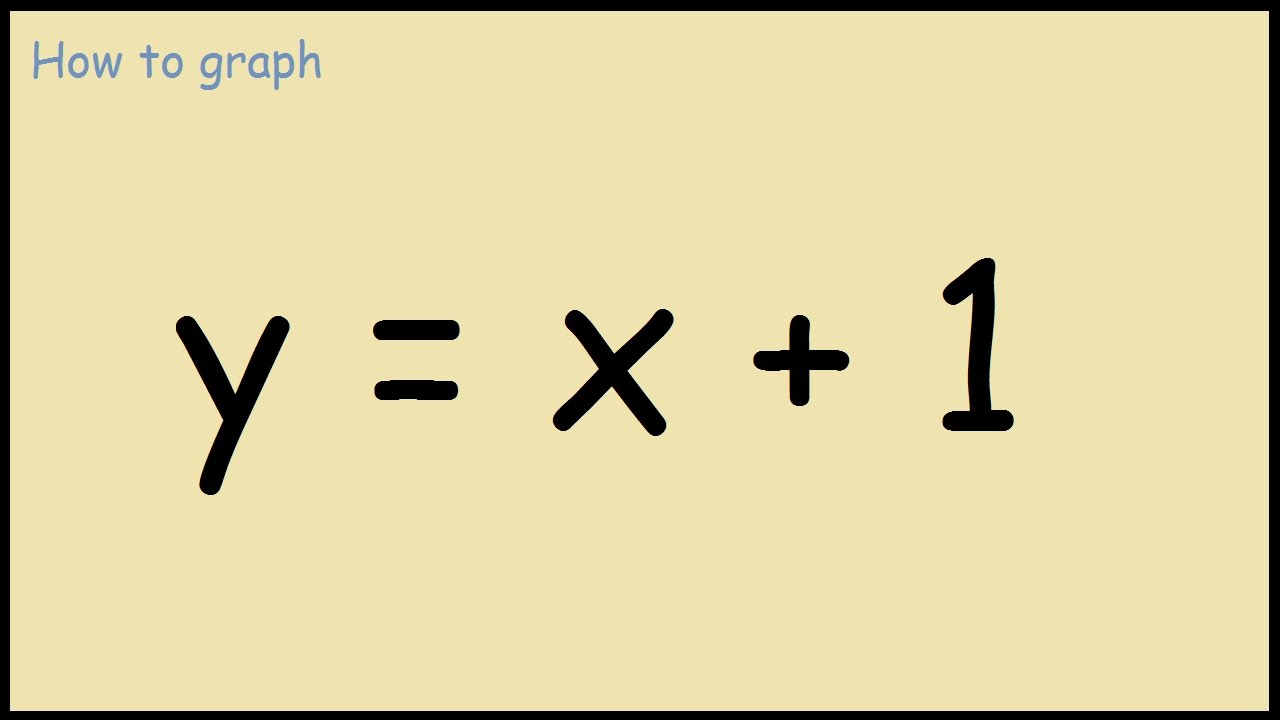


How To Graph Y X 1 Youtube


Graphing Systems Of Linear Equations



Graph Graph Equations With Step By Step Math Problem Solver
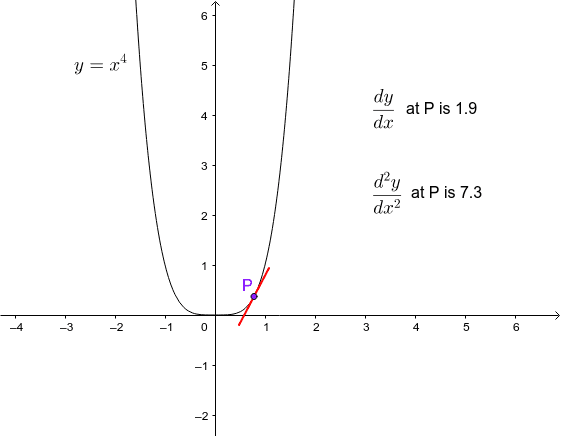


Graph Of Y X 4 Geogebra


Prove The Inequality X X 1 Y Y 1 Xy 1 X X 1 Y Y 1 Xy 1
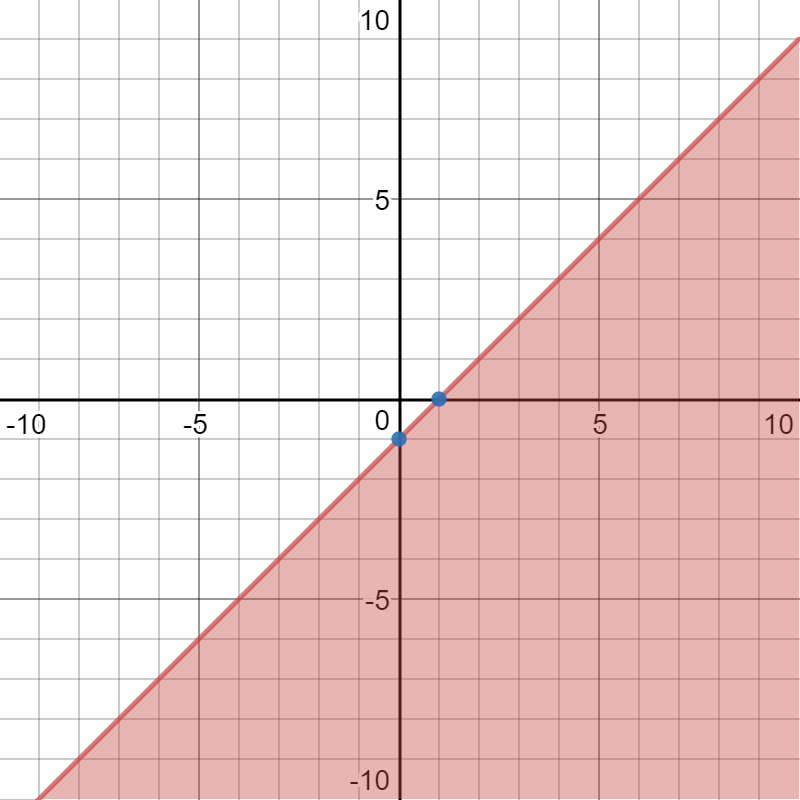


How Do You Graph Y X 1 Socratic
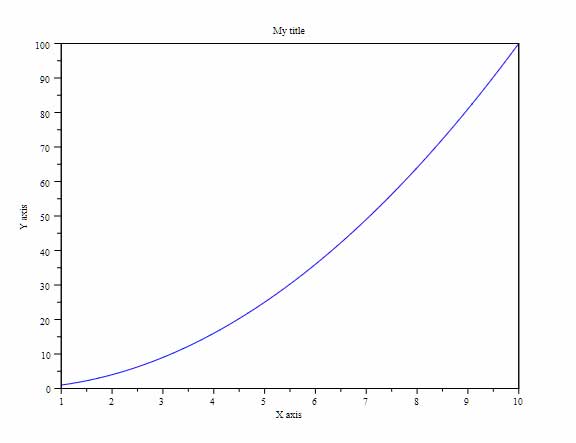


Plotting Www Scilab Org


Modulus Function


